|
Bolise Co., Ltd.
|
what is Fucoxanthine ?
| Payment Terms: | WU,Paypal |
| Place of Origin: | Guangdong, China (Mainland) |
|
|
|
| Add to My Favorites | |
| HiSupplier Escrow |
Product Detail
Fucoxanthin is a type of carotenoid found naturally in edible brown seaweed such as wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and hijiki (Hijikia fusiformis)
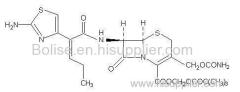
Product name: Fucoxanthine
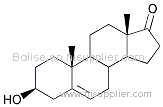
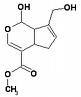
CAS No.:3351-86-8
Molecular weight: 658.91
Molecular formula: C42H58O6
Product description:
Fucoxanthin is a type of carotenoid found naturally in edible brown seaweed such as wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and hijiki (Hijikia fusiformis), which are used widely in Asian cuisine. Wakame is the seaweed used in miso soup.
Fucoxanthin is also found in much smaller amounts in red seaweed (the kind typically used in Japanese sushi rolls) and green seaweed.
Why Do People Use Fucoxanthin
So far, scientific support for the potential health benefits of fucoxanthin is lacking.
1) Weight Loss
Fucoxanthin is being explored for weight loss. So far, only animal studies have been done. Japanese researchers have found that fucoxanthin (isolated from wakame) promotes the loss of abdominal fat in obese mice and rats. Animals lost five to 10% of their body weight.
Although it's not fully understood how fucoxanthin works, it appears to target a protein called UCP1 that increases the rate at which abdominal fat is burned. Abdominal fat, also called white adipose tissue, is the kind of fat that surrounds our organs and is linked to heart disease and diabetes.
Although it's promising and already a popular nutritional supplement, more research is needed to determine if fucoxanthin will work in the same way in humans. If it does prove to be effective, fucoxanthin could be developed into a diet pill for obesity.
2) Diabetes
Fucoxanthin has also been found in animal studies to decrease insulin and blood glucose levels. Researchers hypothesize that fucoxanthin anti-diabetes effect may be because fucoxanthin appears to promote the formation of DHA (the omega-3 fatty acid found in fish oil). DHA is thought to increase insulin sensitivity, improve triglycerides and reduce LDL ("bad") cholesterol.
3) Cancer
Preliminary laboratory research suggests that fucoxanthin may have anti-tumor effects. No studies have looked at whether this holds true in humans or if taken orally.
Caveats
Because there hasn't been research on fucoxanthin in humans, the possible side effects aren't known.
People shouldn't consume large amounts of wakame or other types of seaweed as a source of fucoxanthin. Seaweed is rich in iodine and excessive consumption may result in iodine poisoning. High levels of iodine can interfere with the function of the thyroid gland. Also, consuming excess amounts of iodine-rich foods isn't recommended if there is a known allergy or hypersensitivity to iodine.
Using Fucoxanthin for Health
Due to a lack of supporting research, it's too soon to recommend fucoxanthin for any health condition. Supplements haven't been tested for safety and due to the fact that dietary supplements are largely unregulated, the content of some products may differ from what is specified on the product label. Also keep in mind that the safety of supplements in pregnant women, nursing mothers, children, and those with medical conditions or who are taking medications has not been established. You can get tips on using supplements here, but if you're considering the use of fucoxanthin, talk with your primary care provider first. Self-treating a condition and avoiding or delaying standard care may have serious consequences.